Introduction
Several times we encounter a great and sophisticated web or desktop application
that does not poses it's appropriate market share just for the reason of poorly
written SETUP package and poorly designed deployment strategy. The fact is simple:
If your users are not able to easily deploy your application then whatever sophistication
or features you provide, they will be unable to even experience your application
from the very first place!
In this tutorial we are going to show you a set of techniques by which you can package
and deploy your web applications .....
Alternatives
When it comes to web applications specifically, then you will encounter many techniques
that can be utilized as a deployment strategy for your web application:
XCOPY Deployment
The most trivial technique is to simply copy your web application files to the production
server hard drive and set a virtual directory there. The setting of a virtual directory
is needed by several deployment schemes and can be achieved from Internet Information
Manager Microsoft Management Consol (MMC snap-in). Because developers typically
use the command line order 'XCOPY' to implement this technique, this technique is
typically referred to as XCOPY Deployment.
Copy Web Site
Copy Web Site is a new technique provided in ASP.NET 2.0 and Microsoft
Visual Studio 2005 (Available from the Website / Copy Web Site... Menu option).
Although this technique is performed from inside Visual Studio (in contrast with
the XCOPY deployment technique which is performed from outside Visual Studio), there
is no compilation performed at all. All your pages are still in their source code
form on the production server. Some developers see this fact as a high risk on their
intellectual property. Two extra disadvantages of this technique (and in fact any
other technique that does not involve any compilation before deployment) are reduced
error checking and the slow initial page load.
The reduced error checking is a direct result to that no compilation is performed
and hence some errors may be discovered by your users later. The initial page load
slowness is also because nothing is compiled yet and the entire web application
has to be compiled at the time the first page is being requested. An advantage of
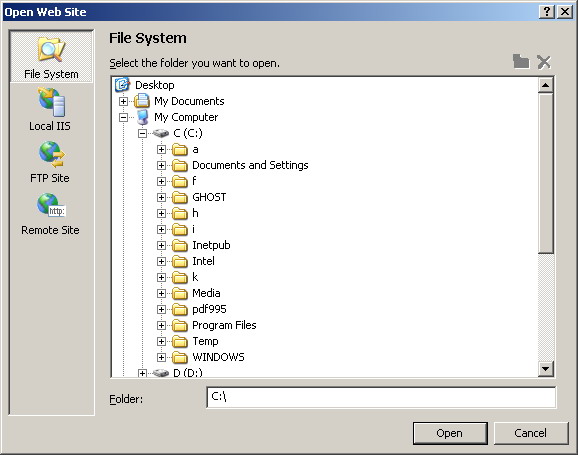
this technique over the XCOPY deployment is that you have the options to deploy
to the File System, the Local IIS, the FTP Sites, and the Remote Sites. Please see
figure 1.
 width="578" /> width="578" />Figure 1 |
Pre-compilation
All of the deployment methods we mentioned so far suffer from the fact of that no
compilation is performed along with the disadvantages that comes as a direct result
from this fact. To ensure fast page load and some protection of your source code,
you should pre-compile your web site before deployment.
Pre-compilation can be performed in-place by just adding '/Deployment/Precompile.axd'
to the root URL of your web application and opening the resulting URL in Internet
Explore.
Pre-compilation can also be achieved using the command line compiler 'aspnet_compiler'.
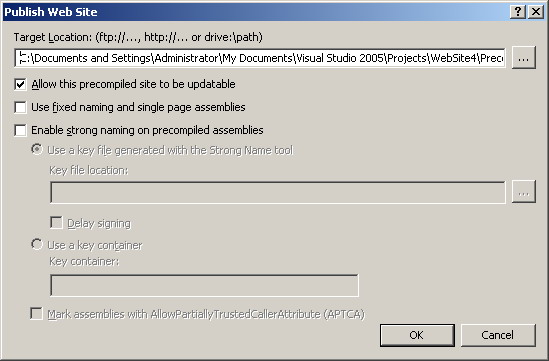
Using Microsoft Visual Studio 2005 you can still perform pre-compilation from the
'Build / Publish Web Site' menu command. Please see figure 2.
 width="549" /> width="549" />Figure 2 |
SETUP Projects
src="http://www.beansoftware.com/ads/LQ-Rectangle.aspx" width="336">
It's always desirable to package your web applications such that they are easy to
deploy on the production server. Microsoft Visual Studio 2005 gives you this rich
packaging option for free ... Just follow the following instructions ...
First of all you need to know that our target is to create a package (and MSI file)
that contain our web application in a form that can be later easily deployed on
the final production server.
Let's start by selecting 'File / New / Project' in Microsoft Visual Studio 2005.
This will present you the famous set of possible project types from which you will
select 'Other Project Types / Setup and Deployment' then you will select the 'Web
Setup Project' icon from the side to the right. See figure 3.
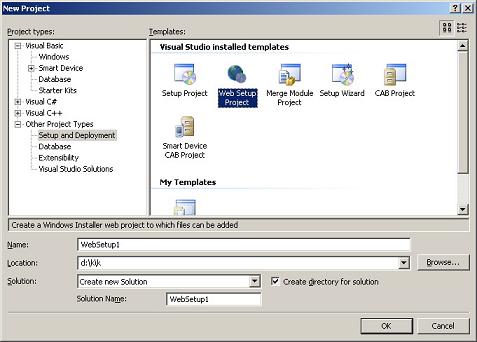 Figure 3 |
In figure 3, set the appropriate project name and folder options then click OK.
You can always have the same behavior by adding the SETUP project above to your
web application solution instead of creating a new separate solution. You can achieve
this by selecting 'File / Add / New Project' instead of 'File / New / Project'.
This way you will have a self contained web solution. The 'File / Add / New Project'
method is much more recommended.
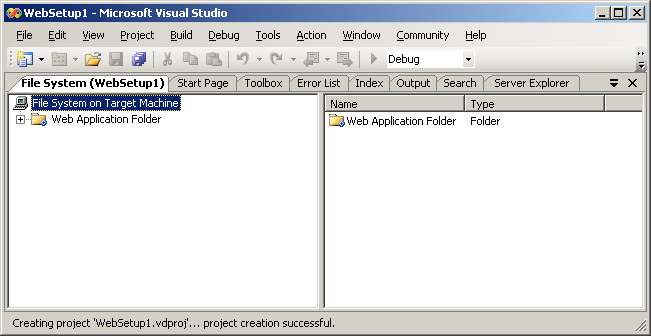
Your setup project will then open as in figure 4 below:
 width="651" /> width="651" />Figure 4 |
You will then need to add your web application files to the SETUP project we are
developing now. This can be achieved by right clicking your SETUP project name in
solution explorer and selecting 'Add / Project Output'. Please see figure 5.
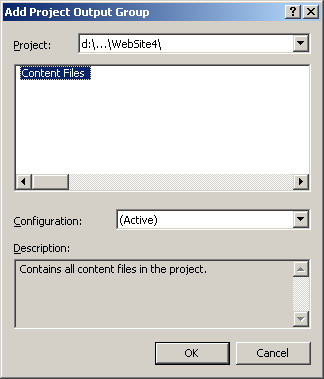 width="324" /> width="324" />Figure 5 |
To tune the properties of our SETUP project, we will need to press F4 while it's
name is selected in the solution explore. This will bring the SETUP project's properties
window. Several useful properties can be set in this window:
Property | Purpose |
Author, Description, Manufacturer, ManufacturerUrl, ProductName, Subject, Title, and Version | Use all of these properties to identify / describe your application and yourself. |
AddRemoveProgramsIcon | Here you can specify the icon to be displayed beside your application in Windows Control Panel's Add Remove Programs. |
DetectNewerInstalledVersion | Specify here whether or not a check is to be performed to determine the existence of a new version already installed of your web application. |
RemovePreviousVersions | Specify here whether you need an older version of your web application to be removed if a newer version is being installed. |
RestartWWWService | Some web applications requires the Internet Information Service to be stopped and then restarted after the deployment of the application. Use this property to control such behavior. |
The last and most important step is to actually build our SETUP project. This cane
be achieved by right clicking the name of our SETUP project in the solution explorer.
It's this specific step that creates the MSI package / file mentioned above. This
is the file you will need to distribute to your users and this is the file they
will use to deploy the web application on their production server.
It's worth mentioning that the actual deployment process will be some what similar
to the SETUP of any typical desktop application (with some exceptions of course).
One of the many similarities is that the web application after deployment will automatically
appear in the 'Add / Remove Programs' window of Windows Control Panel.
For your users to deploy your web application they will just need to double click
the MSI file. This will produce something similar to figure 6:
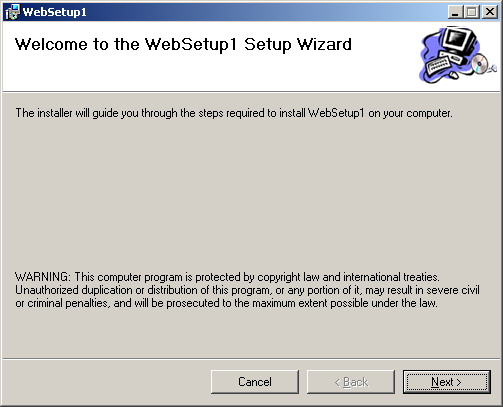 width="503" /> width="503" />Figure 6 |
Protection and obfuscation of .NET executable files (.exe, .dll,...)
You must know that every of your .NET products, web application or ASP.NET custom
control, can be easily decompiled. Practically every user can get your source code
by using some free .Net decompiler. If your license doesn't include source code
it is not enough to just exclude source code files from installation. You need additional
protection.
After long analyze, we decided to use rel="nofollow" target="_top">Spices.Net for protection of all products of
Bean Software. Even if you can't afford complete suite, consider at least their
Obfuscator. Later, I discovered rel="nofollow">.NET Reactor which also looks good and it is about ten times
cheaper :). You can check Product Comparison link on NetReactor site where it is
compared to some other products, it looks really impressive, and not only in price
issue.
For further information
Refer to the online copy of Microsoft Developers Network at
http://msdn.microsoft.com or use your own local copy of MSDN.
No comments:
Post a Comment